Return to Index |
Previous Image |
Next Image |
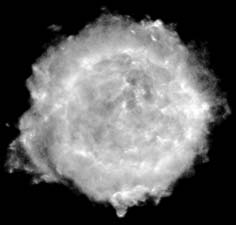
Cassiopeia A is
the youngest known supernova remnant in the Milky Way Galaxy. A supernova
remnant is the outer shell of gas ejected by a dying star into interstellar
space. Astronomers have calculated that the supernova associated with
Cassiopeia A must have exploded around the year 1667. Cassiopeia A is
located about 10,000 light-years from Earth. Supernova explosions such
as this are responsible for producing most of the heavier elements in
the universe, such as Carbon and Oxygen, that make Carbon based life possible.
Only these collapsing stars reach temperatures high enough to fuse hydrogen
and helium into heavier metals. Cassiopeia A has been found to be rich
in iron, silicon, and sulfur. The star exploded to form Cassiopeia A was
about ten times more massive than our own sun. The gaseous shell formed
in the explosion is about 10 light years in diameter. (Courtesy of National
Radio Astronomy Observatory's Very Large Array
of radio telescopes)
References:
http://www.seds.org/~spider/spider/Vars/casA.html
http://antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov/apod/ap000103.html
http://chandra.harvard.edu/xray_sources/casa.html
Animation of Contrast
Object |
Distance from Earth |
Wavelength |
Cassiopeia A |
10,000
light years |
Radio |